
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition).
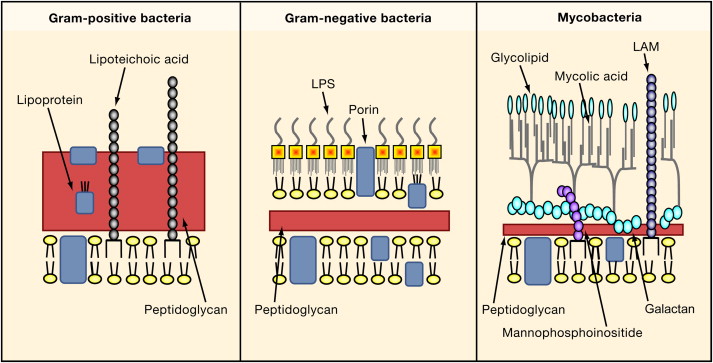
Madigan Michael T, Bender, Kelly S, Buckley, Daniel H, Sattley, W.Coagulation (DIC) is mediated through the activation of Hageman factor (coagulation factor XII).Damage to the endothelium from bradykinin-induced vasodilation leads to shock.Macrophage activation and products lead to tissue damage.LPS activates macrophages, leading to the release of TNF-alpha, IL- 1, and IL-6. IL- 1 is a major mediator of fever. Lipopolysaccharide is a pyrogenic (responsible for fever) substance, and also causes endotoxic shock.Outer membrane allows transport of smaller molecules, such as nucleotides, oligosaccharides, monosaccharides, peptides, and amino acids, to pass across via porin channels.

It also serves as a barrier to various external chemicals and enzymes that could damage the cell. Outer membrane serves as an impermeable barrier to prevent the escape of important enzymes, such as those involved in cell wall growth, from the periplasmic space.Functions of Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) Layer Note: LPS is heat stable and not strongly immunogenic so it cannot be converted to a toxoid.
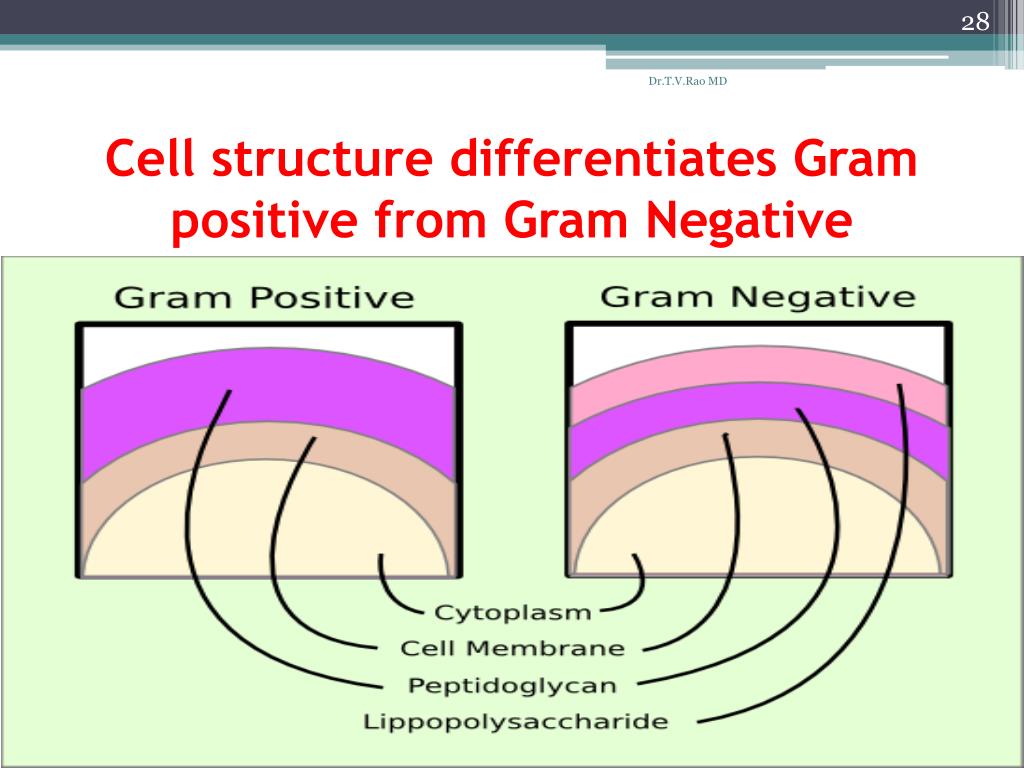
O antigens are used to identify certain organisms in microbiology laboratories. O antigens are toxic and account for some of the virulence of certain gram-negative bacteria. O antigen is highly varied among species.Įxample: E.coli O157:H7 which causes food poisoning and hemolytic uremic syndrome. LPS from non-pathogenic bacteria has been studied in detail to discover new therapeutics to combat lethal bacterial infections 4. O antigen: An outer polysaccharide consisting of up to 25 repeating units of 3-5 sugars. Gram-negative bacteria are characterized by the presence of a unique cell wall component termed lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which is associated with substantial diseases in humans and marine organisms.A core polysaccharide of five sugars linked through ketodeoxy-octonate (KDO) to lipid A.Also known as endotoxin, it is responsible for toxic effects (fever and shock). Generally, it is not released until the death of a cell.Įxception: Neisseria meningitidis, which over-produces outer membrane fragments. A phospholipid called Lipid A embeds in a lipopolysaccharide layer in the outer leaflet.The LPS is composed of three distinct units All rights reserved.Cell wall structure of Gram-negative bacteria (Image source: ) These studies are significant not only for common therapeutic against mixed biofilms, but for better understanding of bacterial interactions within natural or host infection environment as well.Īdhesion Amyloid proteins Biofilms Gram-negative Gram-positive Quorum sensing.Ĭopyright © 2021 Elsevier GmbH. However, quorum sensing (QS) may play a common regulation during biofilms dispersal. Genetic regulation by c-di-GMP is prominent in Gram-negative bacteria. An additional common feature is the presence of membrane vesicles, and the potential of these vesicles requires further investigation. Enzymatic degradation of matrix components by glycoside hydrolase and DNase (nuclease) may disrupt both Gram-type biofilms. The inhibition of the polymerization of amyloid-like proteins might impact the biofilms of both Gram-type bacteria. The Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and cell wall glyco-polymers of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria seem to play similar roles during initial adhesion. We tried to focus on common components which exist at each stage of biofilm development and regulation. Thus, a greater understanding of the conserved themes in biofilm formation is required for common therapeutics.
Many biofilm studies examine specific Gram type cultures, whereas nearly all biofilm communities in nature comprise both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Biofilms are root cause of industrial biofouling and characterized by antimicrobial resistance during infections. The Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria are attributable to matrix-enclosed aggregates known as biofilms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
